Have you ever wondered if cold sores and HSV-1 are one and the same? Well, wonder no more! In this article, we will explore the relationship between cold sores and HSV-1, and unravel the mystery behind these pesky little blisters. Get ready to learn more about the root cause of cold sores and how they are connected to the Herpes Simplex Virus type 1. So sit back, relax, and prepare to gain a clearer understanding of cold sores and the virus behind them.


Understanding HSV-1
What is HSV-1?
HSV-1, which stands for Herpes Simplex Virus type 1, is a common viral infection that primarily affects the mouth and face. It is commonly known as oral herpes or cold sores. HSV-1 is a contagious virus that can cause painful blisters or sores on or around the lips, in the mouth, or on the face. It is important to note that HSV-1 can also be responsible for genital herpes, although HSV-2 is the more common cause of genital herpes.
How is HSV-1 transmitted?
HSV-1 is highly contagious and can be easily transmitted through direct contact with an infected person. The virus is commonly spread through oral secretions such as saliva, meaning that sharing utensils, kissing, or coming into contact with the infected person’s saliva can lead to transmission. It can also be spread through skin-to-skin contact, such as during oral sex. Furthermore, HSV-1 can be transmitted even when there are no visible sores or symptoms present, making it important to take precautions to avoid transmission.
What are the symptoms of HSV-1 infection?
When a person is initially infected with HSV-1, they may experience a variety of symptoms. These can include fever, sore throat, swollen glands, and mouth ulcers. After the initial infection, the virus remains dormant in the body and can cause recurrent outbreaks of cold sores over time. These outbreaks typically involve the appearance of painful blisters or sores on or around the lips, mouth, or face. The sores can be accompanied by sensations of tingling or itching before they appear. The intensity and frequency of outbreaks can vary from person to person.
How common is HSV-1?
HSV-1 is incredibly common, with a large portion of the global population being infected with the virus. In fact, it is estimated that around 67% of the global population under the age of 50 has HSV-1. The virus is most commonly acquired in childhood through non-sexual contact. While HSV-1 is more prevalent in developing countries, it is also widespread in developed nations. It is important to note that the prevalence of HSV-1 infection can vary depending on factors such as geographical location and socioeconomic status.
What are Cold Sores?
What are cold sores and how are they caused?
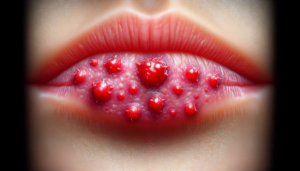
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are small, painful blisters or sores that occur on or around the lips, mouth, or face. They are caused by the HSV-1 virus, which enters the body through direct contact with an infected person. Once the virus enters the body, it remains there for life and can cause recurrent outbreaks of cold sores.
Are cold sores also known as fever blisters?
Yes, cold sores are also commonly referred to as fever blisters. This is because they can be accompanied by symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and swollen glands. The terms “cold sore” and “fever blister” are used interchangeably to describe the same condition caused by HSV-1.
What are the symptoms of cold sores?
Cold sores typically start with a tingling or itching sensation in the affected area, followed by the appearance of small, fluid-filled blisters. These blisters can be painful and may burst, crust over, and eventually heal on their own within a couple of weeks. During an outbreak, individuals may experience discomfort, pain, or burning sensation at the site of the blister. In some cases, cold sores can also be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, headaches, and swollen lymph nodes.
Can cold sores be spread to other parts of the body?
While cold sores primarily appear on or around the lips, mouth, or face, it is possible for the virus to spread to other parts of the body through direct contact. This can happen if a person touches an active cold sore and then touches another area of their body, such as their eyes or genital region. It is important to avoid touching cold sores and to practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of the virus.


Connection between HSV-1 and Cold Sores
Is HSV-1 the sole cause of cold sores?
HSV-1 is the primary cause of cold sores, but it is not the sole cause. While the majority of cold sores are caused by HSV-1, a small percentage of cases can be attributed to HSV-2, which is the more common cause of genital herpes. However, it is important to note that HSV-1 is estimated to be responsible for over 90% of cold sore cases.
Can cold sores be caused by other types of herpes viruses?
Cold sores are primarily caused by HSV-1, but other types of herpes viruses can also contribute to their occurrence. For example, herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), which is responsible for most cases of genital herpes, can occasionally cause cold sores as well. Additionally, herpes simplex virus type 3 (HSV-3), also known as varicella-zoster virus, can cause cold sores in some cases.
Can cold sores be caused by HSV-2?
While HSV-1 is the primary cause of cold sores, HSV-2 can also be a contributing factor. HSV-2 is commonly associated with genital herpes rather than cold sores, but it can occasionally cause cold sores as well. It is important to note that HSV-2 is usually transmitted through sexual contact, while HSV-1 can be transmitted through various types of contact, including non-sexual contact.
Does everyone with HSV-1 have cold sores?
Not everyone with HSV-1 will experience cold sores. After the initial infection, the virus can remain dormant in the body and may never cause any noticeable symptoms. Some individuals may have the virus without ever developing cold sores. However, it is important to be aware that even in the absence of visible cold sores, the virus can still be transmitted to others.
Differentiating HSV-1 Infection and Cold Sores
HSV-1 infection without cold sores
It is possible to be infected with HSV-1 without experiencing cold sores. This is known as asymptomatic HSV-1 infection. In these cases, individuals may have been infected with the virus, but never develop any visible symptoms. Despite the lack of visible sores, asymptomatic individuals can still transmit the virus to others through direct contact or through intimate activities.
Cold sores without HSV-1 infection
While cold sores are usually caused by HSV-1, there are other conditions that can cause similar symptoms. For example, canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are a type of mouth ulcer that can resemble cold sores. Canker sores are not caused by the herpes virus and are not contagious like cold sores. Other conditions, such as impetigo or angular cheilitis, can also cause sores around the mouth that may be mistaken for cold sores.
Testing and diagnostics for HSV-1 and cold sores
If you suspect you have HSV-1 or cold sores, it is recommended to seek medical advice for proper testing and diagnosis. A healthcare professional can perform tests, such as a viral culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR), to confirm the presence of the virus. These tests can be done by swabbing the affected area or by taking a blood sample. Additionally, a visual examination by a healthcare professional can often provide a diagnosis based on the appearance of the sores.

Treatment and Management
Over-the-counter remedies for cold sores
There are several over-the-counter remedies available to relieve the discomfort and promote healing of cold sores. These can include topical creams or ointments containing antiviral agents such as docosanol or benzocaine. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate the pain associated with cold sores. It is important to carefully read and follow the instructions provided with these products.
Prescription antiviral medications
In some cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe antiviral medications to manage cold sores. These medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir, work to inhibit the replication of the virus and can help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks. They are most effective when taken early on at the first signs of an outbreak. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate prescription and usage instructions.
Home remedies and natural treatments
Alongside medical treatments, there are also various home remedies and natural treatments that can help manage cold sores. These can include applying a cold compress to the affected area to reduce inflammation, using aloe vera gel or petroleum jelly to moisturize the sores and promote healing, or taking supplements such as lysine or lemon balm extract, which have been suggested to have antiviral properties. However, it is important to note that evidence supporting the efficacy of these remedies may vary, and it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any alternative treatments.
Prevention and lifestyle measures
To prevent the spread of HSV-1 and reduce the frequency of cold sore outbreaks, there are several preventative measures that can be taken. These can include avoiding close contact with individuals experiencing an active outbreak, practicing good hand hygiene, refraining from sharing personal items such as utensils or towels, and avoiding triggers such as excessive sun exposure, stress, or a weakened immune system. It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate rest, as these can support a strong immune system.
Get 51% Discount If You Order Now!

Complications and Risks
Complications of HSV-1 infection
While HSV-1 infections generally do not cause serious health complications, there can be rare instances where complications may arise. For example, the virus can potentially spread to the eyes and cause a condition called herpes keratitis, which can lead to vision problems if left untreated. In individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, severe HSV-1 infections can occur and may require medical intervention. Additionally, in very rare cases, HSV-1 infection can cause inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), which can be a life-threatening condition.
Potential complications of cold sores
While cold sores themselves are usually not considered serious, they can cause discomfort and pain during outbreaks. The sores can also be a source of embarrassment or self-consciousness for some individuals. Additionally, cold sores can lead to secondary bacterial infections if the skin is broken and bacteria enter the sores. These secondary infections can prolong healing time and may require medical treatment.
Risk factors for severe or recurrent cold sores
Certain factors can increase the risk of experiencing severe or recurrent cold sores. These can include having a weakened immune system, such as due to illnesses like HIV/AIDS or autoimmune conditions, experiencing high levels of stress, or having a history of frequent cold sore outbreaks. It is important for individuals with these risk factors to take extra precautions and seek medical advice for appropriate management strategies.
Preventing Transmission
Reducing the risk of HSV-1 transmission
To reduce the risk of transmitting HSV-1 to others, there are several measures that can be taken. These include practicing good hand hygiene, especially after touching cold sores or areas that may come into contact with them, avoiding close contact with others during active outbreaks, refraining from sharing personal items such as utensils or lip balm, and abstaining from sexual activity during outbreaks. It is important to have open and honest communication with sexual partners to discuss any potential risks or concerns.
Preventing transmission of cold sores
To prevent the spread of cold sores to other parts of the body, it is important to avoid touching the sores and to practice good hygiene. This includes washing hands thoroughly after touching cold sores, using separate towels or tissues to gently pat the affected area, avoiding picking or scratching the sores, and refraining from kissing others or engaging in intimate activities during an active outbreak. Taking these precautions can help reduce the risk of self-infection or transmission to others.
HSV-1 and Cold Sores in Children
How do children commonly contract HSV-1?
Children commonly contract HSV-1 through non-sexual contact with infected individuals. This can occur through sharing utensils, cups, toys, or other objects contaminated with the virus. Additionally, close contact, such as hugging or kissing, with an infected person during an active outbreak can also lead to transmission. Children can also acquire the virus from their mothers during childbirth if the mother has an active genital herpes infection.
Are cold sores more severe in children?
Cold sores in children can vary in severity and duration. Generally, the first outbreak of cold sores in children can be more severe and can be accompanied by flu-like symptoms. With subsequent outbreaks, however, the symptoms tend to be milder and the duration of the outbreak may be shorter. It is important to seek medical advice if cold sores in children are causing significant discomfort or if there are concerns about the child’s overall health.
Managing HSV-1 and cold sores in children
If a child has been diagnosed with HSV-1 or frequently experiences cold sore outbreaks, there are several management strategies that can be implemented. These can include teaching the child good hand hygiene practices, providing their own personal items to avoid sharing, and educating them about the importance of not touching or scratching the sores. It is also important to monitor the child’s overall health, ensure they receive adequate rest and nutrition, and seek medical advice for appropriate medical treatments if necessary.
Psychological and Social Impact
Stigma and misconceptions surrounding cold sores
Cold sores can carry a social stigma due to misconceptions and misunderstandings about the condition. Some people may mistakenly associate cold sores with promiscuity or uncleanliness, despite the fact that HSV-1 can be contracted through non-sexual contact. This stigma can lead to feelings of embarrassment, shame, or isolation in individuals who experience cold sores.
Psychological effects of living with cold sores
Living with cold sores can have psychological effects on individuals, particularly if the outbreaks are frequent or severe. Cold sores can cause physical discomfort, pain, and sometimes visible cosmetic changes, which can impact self-esteem and body image. The fear of outbreaks and concerns about transmission can also cause anxiety or stress. It is important for individuals experiencing these psychological effects to seek support and to remember that cold sores are a common condition that can be managed.
Support and coping strategies
There are several support systems and coping strategies available to help individuals manage the psychological and social challenges associated with cold sores. Support can come from healthcare professionals, support groups, or online communities where individuals can share their experiences and receive advice or encouragement. Additionally, practicing self-care, maintaining a positive mindset, and educating oneself and others about cold sores can also contribute to overall well-being and improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding HSV-1 and cold sores is essential in managing and preventing the spread of this common viral infection. HSV-1, which causes cold sores, is highly contagious and can be easily transmitted through direct contact. While cold sores can cause discomfort and occasional complications, proper treatment, prevention, and management strategies can help reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. It is important to seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Remember, you are not alone in dealing with cold sores, and with the right information and support, you can effectively manage and live well with this condition.